
A Earthquake of magnitude 3.5 occurred on December 25th in the community foothillswhich, according to the, is located in the department of Santander Colombian Geological Survey (SGC).
The earthquake began at 12:31 a.m. (local time) and had a depth of 158 kilometers, with a latitude of 6.867274761 and a longitude of -72.99977112.
It is worth noting that this information released by the SGC is preliminary and may be subject to changes or updates regarding both the magnitude of the quake and the exact location of its origin.
In Colombia the Earthquake intensity It is measured using the European Macroseismic Scale (EMS-98), which starts at intensity 2, described as “hardly any meaning” of very few people at rest; Level 3 is classified as “easily noticeable”where vibrations of some objects can occur.
An earthquake is considered intensity 4 if this is the case “largely noticeable” by many people inside buildings and by few outside. Windows, doors and dishes vibrate. At level 5, “strongly noticeable”small objects move, doors or windows swing, and slight cracks may appear in buildings or houses.
Type 6 intensity implies a “minor damage”in this area some people may lose balance; Some objects fall and many buildings show minor damage. Level 7 occurs when a “moderate damage”That means heavy furniture can move, many buildings have cracks, and coatings can fall off the walls.
Finally, at intensities above 7, a “serious damage”: At this time, many people have difficulty standing; heavy objects fall; and old, weak structures can collapse.
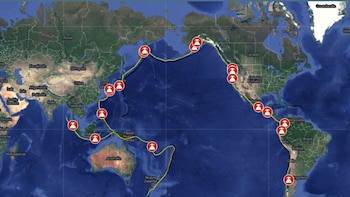
Colombia is considered a country of high seismic risk because it is in the Pacific Ring of Firea region where 75% of the world’s existing volcanoes are concentrated and where approximately 80% of all volcanoes occur. strongest tremors worldwide.
Also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, it consists of the mountainous regions of western Argentina, Chile, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, El Salvador, Honduras, Guatemala, Mexico, the United States and Canada. It then circumnavigates the Aleutian Islands and runs along the coasts and islands of Russia, Japan, Taiwan, the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, East Timor, Brunei, Singapore, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Tonga and Tuvalu and New Zealand.
In the specific case of Colombia, the country lies in two important subduction areas because, on the one hand, it has the Nazca plate with the South American and this last one, which also collides with that Caribbean platecausing it to constantly shake.
Given this situation, the departments of Nariño, Chocó, Caldas and Santander are the places where there is the most tremor; In the latter lies the municipality of Los Santos, which is considered the second the most earthquake-prone area in the world.
Ecuador-Colombia from 1868
On August 15 and 16, 1868, two earthquakes with magnitudes of 6.3 and 6.7 occurred in the border area between Ecuador and Colombia, the latter being the deadliest, lasting almost a minute.
The first of these was recorded in the towns of El Ángel and La Concepción; while the second earthquake completely destroyed the Ecuadorian town of Ibarra. It is estimated that this movement claimed around 70,000 victims in both countries, including dead and injured.
Cúcuta earthquake of 1875
This earthquake, also called the Andean earthquake, occurred on May 18, 1875 and had a magnitude of between 7.5 and 8.5 in Cúcuta, but also caused damage in the neighboring Venezuelan state of Táchira.
Although some claim that the number of victims of this earthquake reached 3,000, only 461 bodies were found, at least in the affected area of Colombia. This earthquake also created hot springs in what are now known as “Agua Hedionda,” “El Tampaco,” and “Aguas Calientes.”

1906 earthquake and tsunami
A magnitude 8.8 earthquake struck Esmeralda province in Ecuador on January 31, on the border with Colombia. This movement triggered a tsunami that claimed 1,500 lives. According to the SGC, the waves reached a height of five meters and left the Tumaco region of Colombia under water.
1994 Páez earthquake
The earthquake occurred on June 6, 1994 in the foothills of the Central Cordillera of the Cauca Andes in southwestern Colombia. It had a magnitude of 6.4 and claimed about 800 lives, mostly residents of settlements near the Páez River. This is considered the second deadliest in the country’s history.
Coffee axis from 1999
This earthquake, considered the most severe earthquake in the country’s recent history, struck the Quindío and Risaralda departments in Colombia, causing more than a thousand deaths.
The earthquake occurred on January 25, 1999 and had a magnitude of 6.2. Several hospitals were affected and resources to deal with the emergency were limited. The earthquake left four thousand people injured and nearly 500 missing.
Around 8,000 coffee plantations were completely or partially destroyed and 13,000 buildings of various companies and industries were affected.



