In recent months, Argentina’s industry has shown increasingly visible signs of Dissimulation and withdrawalwith a sequence of Plant closures, suspensions and layoffs of employees that span multiple production sectors. Although every company usually bases its decisions on internal or strategic reasons, the common denominator is clear: the decline in domestic consumption and the loss of competitiveness in the face of the increase in imports.
A current survey by the consulting company Systemic Put concrete numbers on this process. According to the report In the last quarter, 21 cases were registered of closures, suspensions or staff reductions with immediate effects 4,382 workers. The worst affected areas were Buenos Aires Province, Santa Fe and the NOARegions with a strong industrial weight.
Layoffs and Suspensions: Which Factories Closed Their Doors
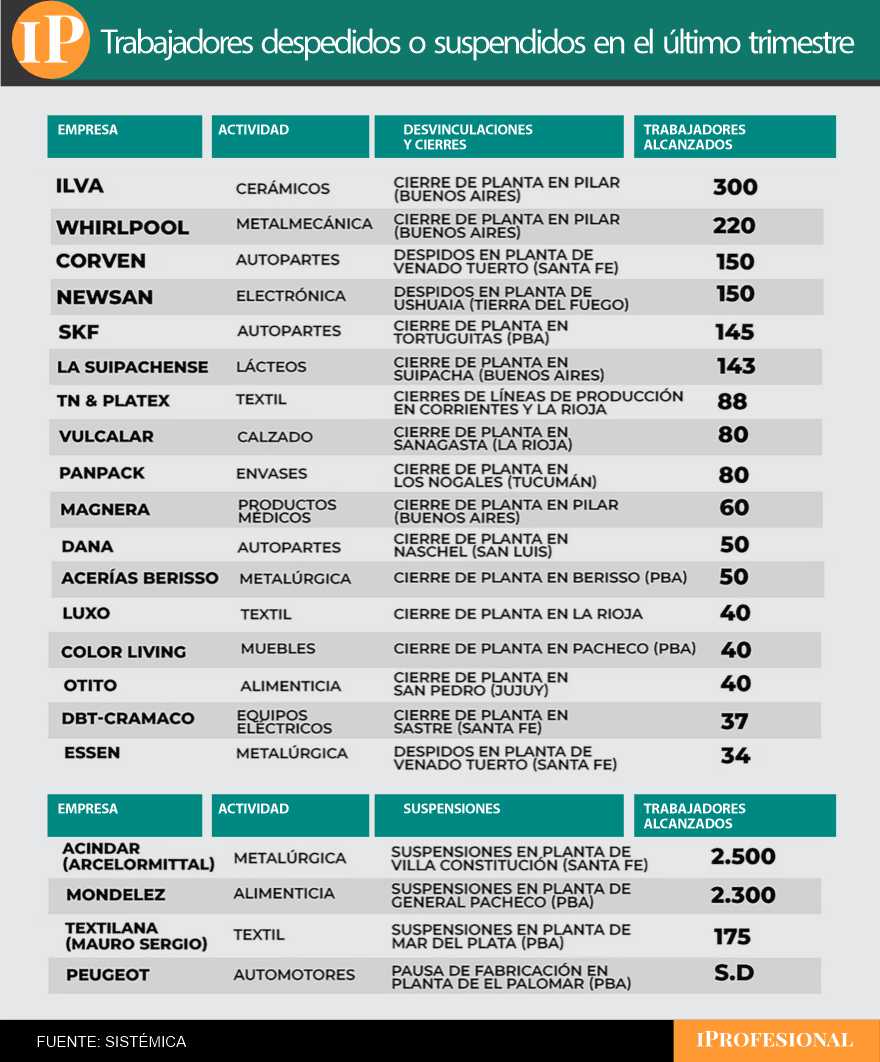
All companies that have closed plants and laid off or suspended employees
The crisis has fully affected the historical sectors of production. In it Ceramics sector, Ilva has closed its factory columnin the Buenos Aires area, and remained unemployed 300 workers. Also in Buenos Aires, the multinational company Jacuzziassociated with the metal processing industry, lowered the blinds of his factory, which was inaugurated in the year 2022with 220 jobs affected.
The category Car participants He wasn’t left out either. Corven pushed ahead with layoffs at its plant One-eyed deerSanta Fe, where 150 workers They lost their jobs. Again, SKF closed his restaurant small turtlesin Buenos Aires, with 145 separationswhile Dana closed his factory naschelSan Luis, what compromised 50 jobs.
In the Electronics industrythe adjustment was clearly noticeable Land of Fire: Newsan fired 150 workers your system Ushuaia. In parallel, the sector electrical devices added the closure of the factory DBT Cramaco In TailorSanta Fe, where they were lost 37 jobs.
The dairy industry also suffered a severe blow. The Suipachense has closed its factory SuipachaBuenos Aires, and remained unemployed 143 employees. The company is in the food sector Otito ordered the closure of its branch Saint PeterJujuy, what is affected 40 workers.
He Textile sectorone of the most sensitive to imported competitionaccumulated several cases. TN and Platex discontinued production lines currents And Riojawith 88 breakupswhile Luxo And Vulcalar closed their factories and generated a balance of 168 people laid off.
Mass closures and extended breaks
In addition to closures and layoffs, the quarter was marked by large-area suspensions. In the metallurgical industry Acindar (ArcelorMittal) introduced suspensions in his work Villa ConstitutionSanta Fe, that achieved 200 workers.
In the food sector Mondelez stopped the activity of 2,300 employees in its facility General PachecoBuenos Aires Province, one of the most significant decisions due to its volume.
In the textile sector again Textilana (Mauro Sergio) exposed 175 workerswhile Stellantis solved bring the holidays forward and extend the summer break a monthuntil the January 4, 2026in its facility The Palomarwhere the models are made Peugeot 208, 2008 and partnersAnd Citroen Berlingo.
Less investment and signs of disinvestment
This deterioration in industrial employment is accompanied by a Decline in foreign direct investment (FDI). According to the exchange balance of the BCRAbetween January and October The net inflow of foreign direct investment recorded a negative balance of $1.5 billionwhich reflects capital outflows and processes Disinvestment of companies already established in the country.
Analysts warn that the phenomenon is a reaction to both warnings macroeconomic and regulatory risksas a Redefining business strategieswith the aim of reducing exposure to markets that are considered more volatile.
“The decline in foreign direct investment is accompanied by an accelerated process of business closures and the shrinking of the local production network. “Announcements of closures, suspensions and layoffs have increased over the past month, with particular impact on industries responding to declines in domestic consumption and import competition,” Sistemica said.
“The phenomenon is not limited to individual cases, but follows a systemic logic: lower demand, higher relative costs and loss of competitiveness form a scenario in which Many companies choose to reduce their operations (generally by switching to import activities) or to withdraw from the market entirely. The result is a deterioration in formal employment and an additional contractionary effect on economic activity, which in turn affects economic fragility,” the report continued.
“The destruction of assets and productive capacity does not allow the redistribution of resources and the creation of new activities in the way that economics textbooks suggest. It leads to job losses and productive waste because capital is not plasticine and workers’ skills are not universal but specific,” the consultancy warned.



