He European Central Bank (ECB) has done its homework and, after cutting interest rates by 200 basis points since June 2024, has managed to reduce inflation very close to its 2% target and boost inflation Economic growth the Eurozone. In this scenario, analysts believe that 2026 will be a year of currency stability and that Eurobank will barely change its interest rates and keep the price of money close to the current 2%.
“With controlled inflation, a solid labor market and fiscal stimulus to reactivate the economy, the ECB is satisfied with the current interest rate level,” say Bankinter analysts They do not expect interest rate cuts for 2026 by the supervisor. They point out that “we only see the risk of another rate cut if the Fed takes a softer approach than expected and encourages excessive appreciation of the euro, which would slow growth and put downward pressure on inflation.”
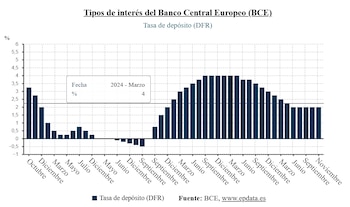
The Governing Council of the ECB kept the three official interest rates stable at its last meeting on December 18th It kept the deposit facility at 2%.that of the main financing operations at 2.15% and that of the marginal credit facility at 2.40%.
With this unanimous decision, the ECB left interest rates unchanged for the fifth month in a row after revising the interest rate upwards Growth forecasts from the euro zone: 1.4% by 2025, compared to the forecast of 1.2% in September; 1.2% in 2026, compared to the estimated 1%, and 1.4% in 2027, compared to the previous 1.3%. It expects a comeback of 1.4% in 2028.
The main catalyst for these increases will be “demand,” according to the president of the European Central Bank. Christine Lagardein the press conference after the December meeting of the Governing Council.
“The economy has shown it ResilienceLagarde said, with growth of 0.3% in the third quarter, mainly due to the strengthening of the market consumption and investment. Other factors in favor are the increase in exports, especially of chemical products, as well as the service sector, “particularly the information and communications sector,” explained Lagarde, for which government spending on infrastructure and defense will continue to support the growth of the euro zone.
However, he warned that “the challenging environment for World trade It will potentially slow eurozone growth this year and next.” Regarding inflation, the issuer’s estimates suggest an increase in 2026. He predicts the general rate will be 2.1% in 2025, 1.9% in 2026, 1.8% in 2027 and 2% in 2028.
Regarding the future monetary policy of the Eurobank, Lagarde did not want to get involved, pointing out that “we simply cannot offer any guidance” and that the situation of interest rates is not static and that it will decide what to do depending on what is happening in the economy.
In this context, analysts forecast for 2026 minimal interest rate movements and that the manager practically stays inside “Pause mode”. However, a minority assumes that there could be another fall in interest rates.
“We continue to hope that the ECB Cut official interest rates by 25 basis points at the March 2026 meeting. And we continue to think it is more likely that there will be two rate cuts in the next 18 months than one rate hike,” he says. Rubén Segura-CayuelaBank of America’s chief economist for Europe.
While, Konstantin VeitPortfolio manager at Pimco, predicts that “official interest rates will rise.” keep unchanged in the near future“But we remain open as to which direction the next measure will take.” He argues that the ECB remains in a “good position”, with inflation close to target and robust growth at levels similar to trend levels.
For this reason, he believes that “it is likely that the majority of members of the Governing Council of the ECB consider that the official interest rate is 2% in the EU.” Center point of a neutral areaHe emphasizes that “the market has fully priced in any further monetary easing and is now in line with our view.” the cut cycle ends at 2%“.
Sandra RhoumaVice President and European Economist of AllianceBernstein’s Fixed Income Team, predicts that domestic disinflation, Euro strength and changes in global trade could exert strong disinflationary pressures from 2026, so “I continue to expect the ECB to take action.” a cut in 2026as I expect more modest growth and increased risk of it falling short of target.”
However, Rhouma points out that if, on the contrary, the ECB’s forecast is correct and growth exceeds potential in 2027 and 2028 and inflation returns to the target, “then…” No additional cuts would be justifiedIt recognizes that fiscal spending and stronger growth would help the ECB achieve price stability in the medium term and “keep its interest rates close to the upper end of the neutrality estimates, i.e.
As for one possible increase short-term interest rates, Annalisa PlazaFixed Income Research Analyst at MFS Investment Management, says unlikely: “It remains low as uncertainties dominate the outlook.” He emphasizes that Lagarde avoided supporting the aggressive comments of other members of the ECB, which “suggests a consensus to maintain the current direction of monetary policy.” In his opinion, the unanimous decision to keep interest rates unchanged and maintain flexibility suggests this There will be no upcoming changes in the policy mix.
Nachu ChockalingamChief Credit Officer at Federated Hermes believes so The situation should be become much worse that the ECB will cut interest rates again in 2026.


