The expert explains what to do
Children are more vulnerable to poison, so pay close attention to the symptoms.
Spider bites in children require immediate attention. Although most species do not pose a serious risk, some contain poisons that can harm health, making them medically important. Currently, the Ministry of Health warns that spiders are the second cause of poisoning by venomous animals in Brazil, behind scorpions. This is why Pequeno Príncipe, which is the largest and most comprehensive pediatric hospital in the country, warns of the importance of parents and guardians being aware of the signs that may indicate a bite.
Pediatric dermatologist Flavia Prevedello, from the hospital, explains that children’s low weight increases the concentration of the poison in the body, making them more vulnerable. “Depending on the species involved and the amount of venom introduced, they may present with systemic symptoms. Therefore, any suspicion should be urgently evaluated in emergency care.”
What are the most dangerous spiders in Brazil?
According to the Ministry of Health, three groups of spiders cause serious accidents in Brazil: the armored spider (Phoneutria), the brown spider (Loxosceles) and the black widow (Latrodectus).
The armored spider is considered the most aggressive and has a painful bite, just like the black widow. The brown spider, on the other hand, is not aggressive and bites when squeezed, often inside clothing, towels, shoes or bedding. Phoneutria and Loxosceles spiders, previously restricted to forests, have begun to occupy urban environments and homes, while Latrodectus lives in the open areas of cities, remaining in their webs and falling to the ground when disturbed.
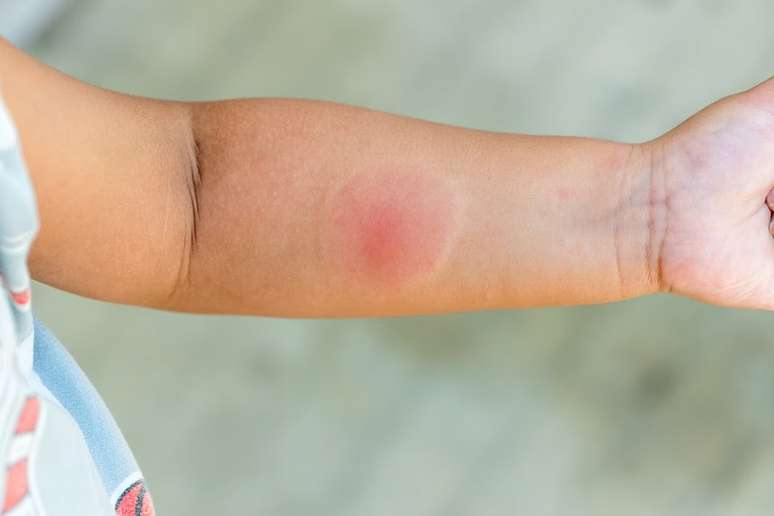
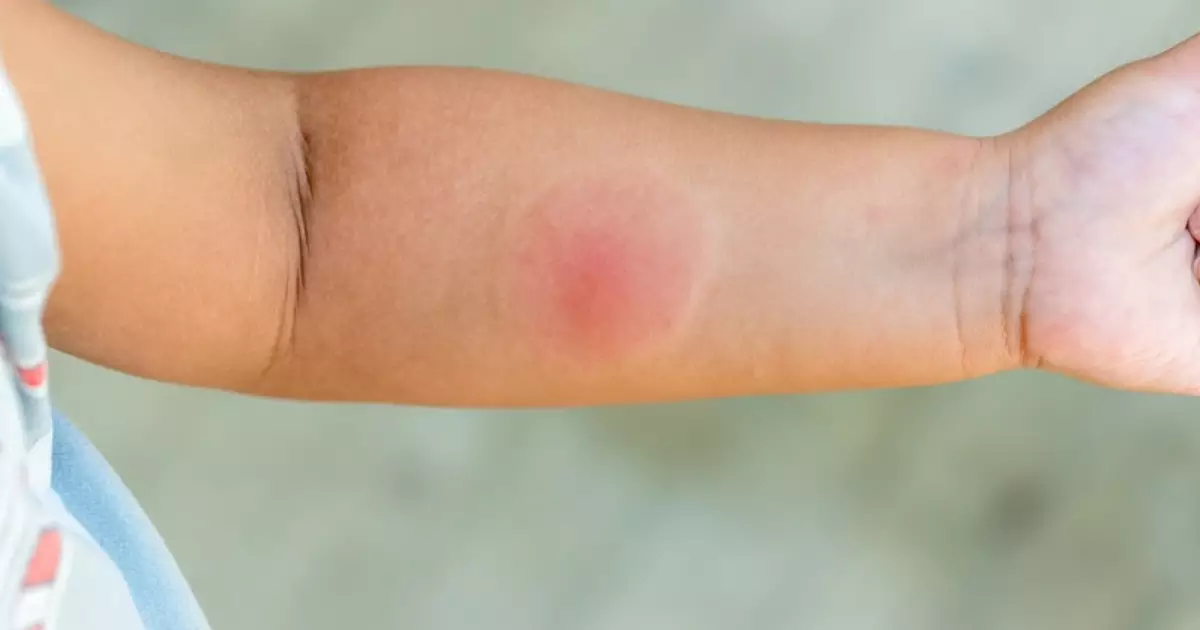
How to identify spider bites in children?
The intensity of reactions is directly related to the dose of poison introduced, which can cause:
- Pain in the area (intense in armadeira and black widow stings);
- Purplish lesion which worsens in 24-72 hours, with risk of necrosis (characteristic of the brown spider);
- Redness and swelling;
- Vomiting and sweating;
- Muscle tremors or spasms;
- Restlessness, malaise or drowsiness.
ATTENTION! In the event of an emergency, contact SAMU (192) or the firefighters (193). Furthermore, the Toxicological Information and Assistance Center (CIATox) has doctors and nurses who provide advice in the event of accidents with venomous animals and other poisonings by calling 0800 644 6774.
What to do if a child has a spider bite?
When noticing a spider bite in a child, the dermatologist advises a few actions:
- Wash the area with soap and water;
- Place a cold compress on the area to relieve pain;
- Seek emergency care immediately;
- Photograph or tell the healthcare professional as many characteristics as possible, such as type, color and size.
Furthermore, the specialist emphasizes that antiarachnoid serum is indicated in the event of systemic manifestations. Updating the tetanus vaccine must be carried out according to medical advice.
How to avoid spider bites?
Spiders tend to take shelter in dark, unused places, such as cracks, rubble, piles of wood, accumulated leaves, and stored clothing and shoes. To reduce the risk of accidents, follow the specialist’s recommendations:
- Keep yards and environments clean and free of debris;
- Seal cracks, holes and drains;
- Check clothes and shoes before using them;
- Move cribs and beds away from walls;
- Do not let bedding touch the floor;
- When outdoors, wear closed shoes and clothing that protects your skin.