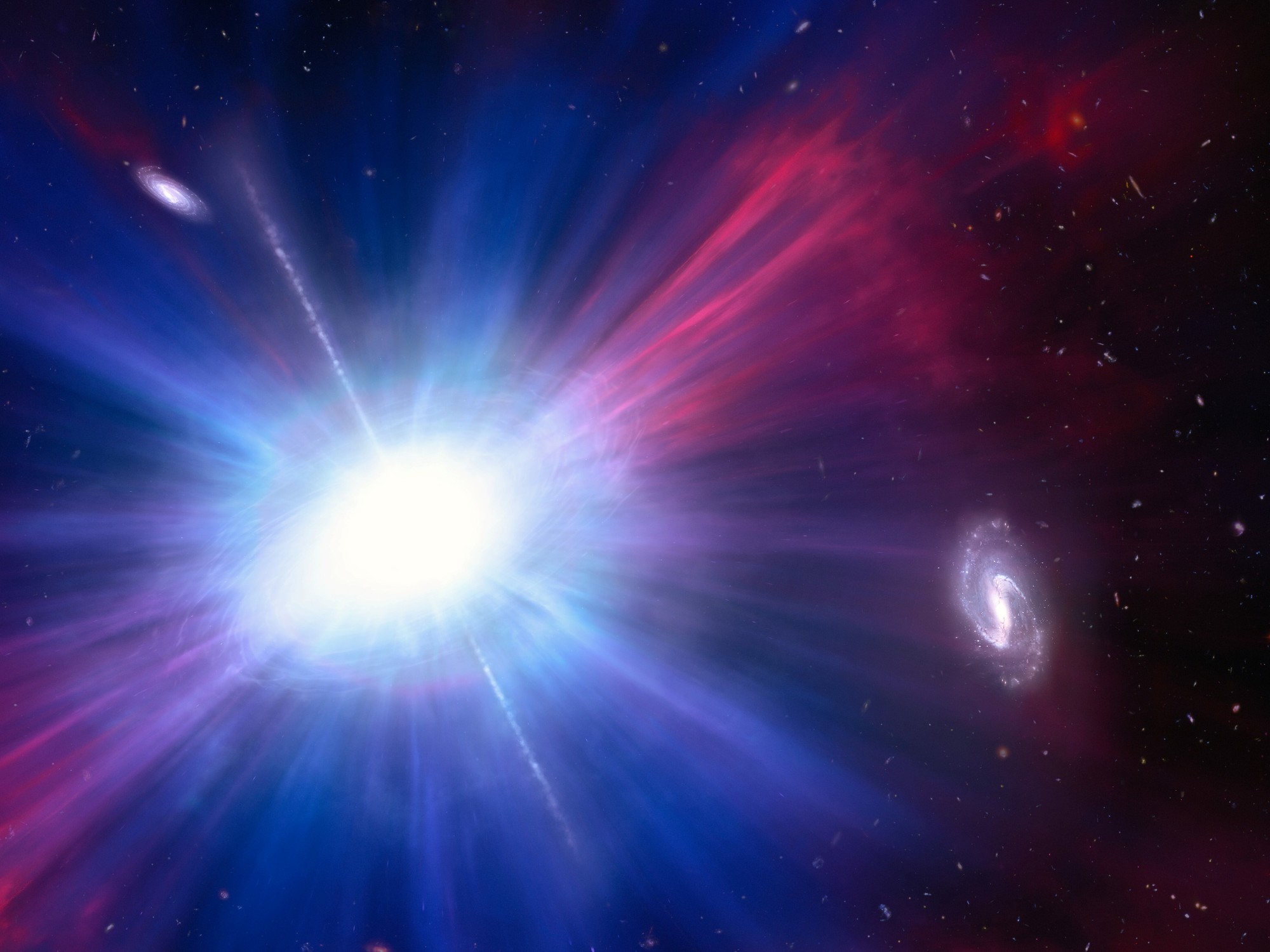
Astronomers have been able to create movies of the night sky, with longer exposures that capture more light than traditional photographs. In this way, they were able to identify bursts of extremely bright blue light.
The discovery began in September 2022, when they noticed a sudden flash of absolutely stunning brilliance through a telescope in Southern California. “The event was about 10 billion times more powerful than the Sun and occurred in a galaxy located a billion light-years from Earth.” The National Geographic website explains:.
After observing the explosion area in detail, astronomers noticed that the event was similar to other explosions, known as fast bright blue light transients (LFBOTfor its abbreviation in English).
A study conducted by Anna Ho of Cornell University and her colleagues Zwicky Transit Facilitya group of telescopes, published in the scientific journal nature Resolves the debate about the origin of these cosmic explosions.
Researchers believe that there is dense stellar remnant (A Black hole or neutron starthe remnants of a massive star’s death) as the driving force for these unusual explosions. “LFTBOTs are approximately ten times brighter than a supernova, but because of their speed, most telescopes do not detect them,” the magazine explains.
In fact, it was LFBOT (or LFTBOT). It was discovered in 2018 It presents strange behavior, with frequent bright flashes, each lasting only tens of seconds. Months after the initial explosion.
Captured with a high-speed optical camera Basic data Which not only confirmed the intensity of the recurring flares, but also provided information about their extremely short duration.
But the discovery he and his colleagues had a huge impact on the scientific community, because, according to National Geographic“No one has ever seen anything like this before, and it expands our understanding dramatically Running violent phenomena in space“.
Naturally, to produce something as powerful, fast, and awesome as LFTBOTs, there has to be a high-powered source. Astronomers have two main suspects: A neutron star or black hole. When a massive star explodes as a supernova at the end of its life, it leaves behind a dense core known as a neutron star; If it is dense enough, it collapses into a black hole.
Scientists wonder if LFBOTs were launched during a period Birth of a built-in objectwhen a star explodes and leaves behind a dense core, or is the product of the renewal of a compact object, such as a black hole, which leads to the disintegration of another star.
“There is speculation that the flares could come from jets emanating from the source, like a lighthouse beam that illuminates the Earth as the object rotates. It could also be due to the magnetic fields of a neutron star, which produce sudden flares, something observed in young neutron stars with a strong magnetic field. Or it could be due to differences in the dense accreting disk of material around the black hole, a phenomenon known to alternate between brightness and dimness,” he says. national geographic, In a long article he published on his website.
However, the exact origin of these eruptions remains a mystery.