The use of Salt in plants sparked current debates in the area of home gardening and home techniques applied to soil care. Different approaches cite this ingredient as a specific resource within routines aimed at controlling external factors and improving specific conditions in specific types of crops.
In addition, there are analyzes too the relationship between salt and insect or snail managementas some gardeners incorporate it as a control tool in affected areas. Interest grew through field experiences that showed some effectiveness in limited areas, but always with precautions.
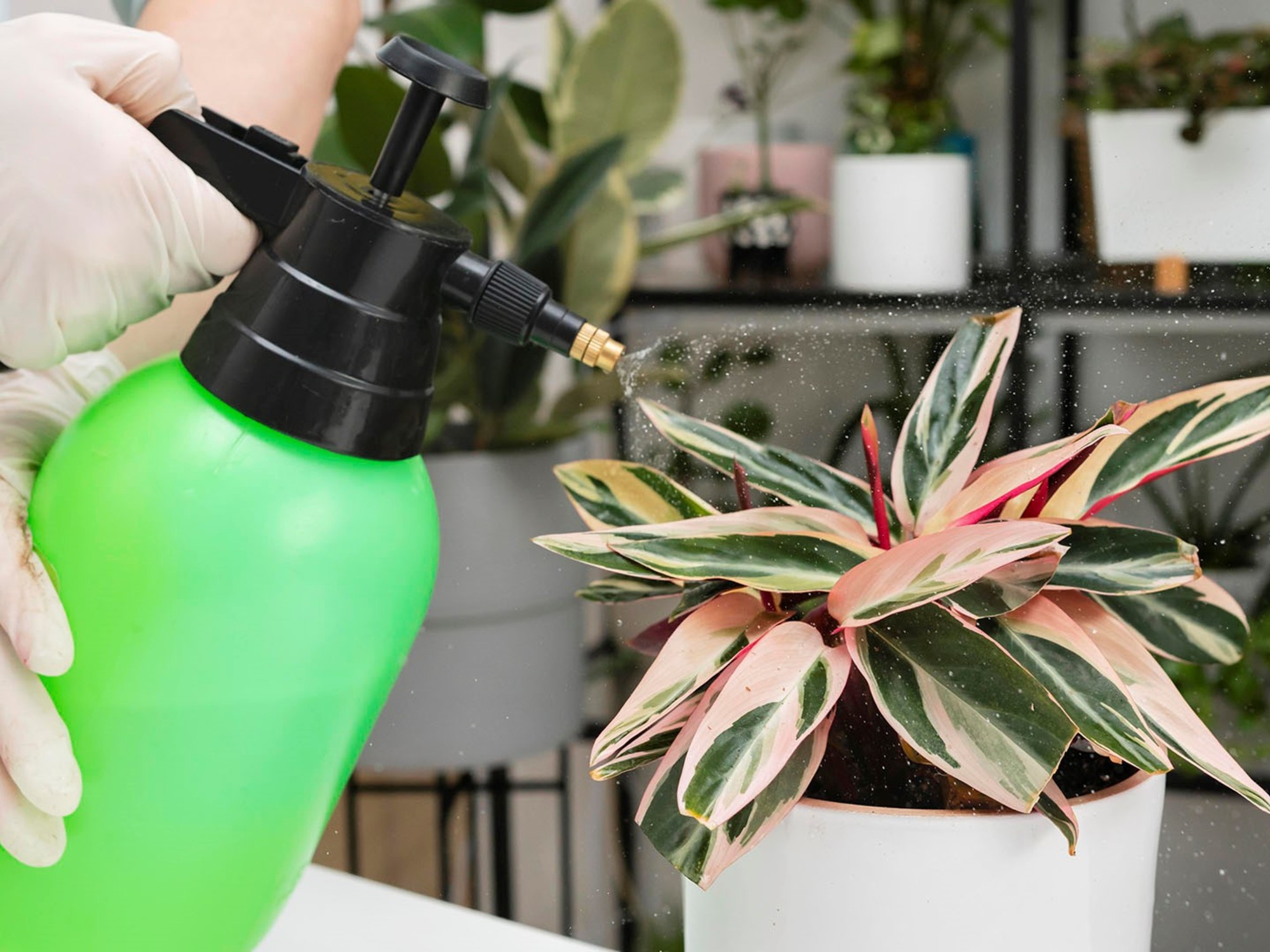
The Apply salt to plants It is usually associated with control tasks in small gardens or on the edges of fields. Its most famous use is Creating barriers that help limit the penetration of snails and other organisms that damage leaves or stems. In these cases, the salt works through contact and is only used in areas outside the crop without touching the plant.
Another specific use is associated with it Soil maintenance in sectors where improvement of surface drainage is sought. Coarse salt, distributed in small amounts and in limited areas, can help reduce stagnant humidity. However, application should be moderate as excessive use risks damaging the soil structure.
Practices incorporating Epson salt (magnesium sulfate) as an occasional supplement are also mentioned in ornamental gardens. This compound is different from ordinary salt and is used in specific cases where the aim is to improve the availability of magnesium in certain crops. Its use seems to be linked to species such as rose bushes or plants that develop yellowish leaves due to a lack of this mineral.
Aside from that, Salt is used locally to clean pots or containers where limestone residue accumulates.. In these cases, it is not applied to the system but to the empty container as part of a maintenance routine. This prevents the formation of deposits that can interfere with proper moisture retention.
The use of salt requires caution due to the sensitivity of the soil to high sodium concentrations. If used excessively, it can interfere with water absorption, harden the soil and reduce nutrient availability. For this reason, it is recommended to limit its use to indirect applications only.
Direct use is completely discouraged in orchards or edible crops. The accumulation of salts can alter root development, alter soil pH, and reduce water holding capacity. On such surfaces, even small amounts can cause damage in the medium term.
Another important aspect is that Interaction between salt and moisture. In very rainy areas, salt applied externally can seep into the subsoil and affect unwanted areas. Therefore, methods that use salt as a pest barrier should only be used on elevated surfaces or edges where contact with rain is controlled.