The breakage of a wooden board left damp and blackened remains next to the Bed of the Tiberand this failure forced an immediate response. Lucio Fabriciothe magistrate in charge of roads, ordered the removal of the damaged elements and the measurement of the passage with ropes and stakes.
The carpenters pointed out the cracks opened by the fire and the floods, and this observation closed the discussion. The decision was oriented towards a factory work that would avoid repeating the same collapse and guaranteed the continuity of the level crossing, which led to a permanent solution.
An urgent intervention activated a change in construction criteria after the deterioration of the approach
He Fabricio Bridge It resulted in the complete replacement of the old passage system and set a clear objective: to ensure daily traffic without interruption. THE choice of stone It responded to the need for stability in the face of fires and floods, thus establishing a criterion of permanence which marked the public works policy. This continuity made it possible to integrate the passage into the urban network and to keep it operational over the centuries.
The urban function was consolidated as direct access to the Tiberina Islandwhere health and religious uses were concentrated, and as a link between busy banks. The crossing accommodated pedestrians and light vehicles without relying on temporary solutions, so daily flow remained stable. This stability favors the organization of space and exchanges, which strengthen economic and administrative life around the river.
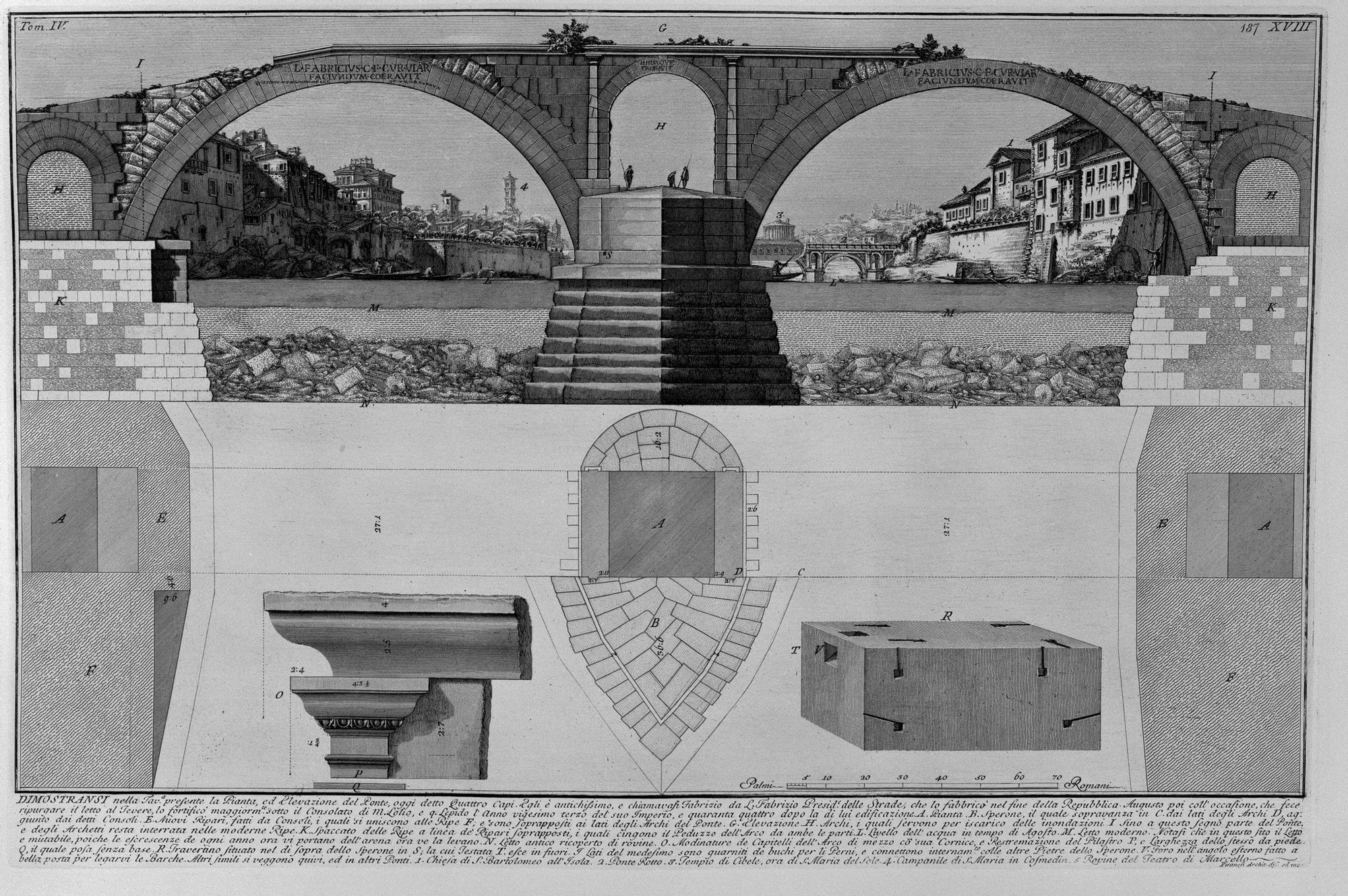
The dimensions of the Fabricio Bridge explain its effectiveness: 62 meters long and just over 5.5 meters wide, with two main arches of approximately 24 to 24.5 meters supported by a central pillar. The height above the water, close to 15 meters, allowed the passage of floods and ancient river traffic. A small drainage arch in the pillar, approximately 6 meters long, relieved water pressure and reduced loads, which protected the structure in the event of flooding.
Authorship was established in 62 BC. C., when Lucio Fabricio, curator of roads, promoted construction after the loss of a wooden bridge. THE the original inscription recorded his responsibility and approval of the workand the immediate reason was the destruction of the previous stage due to fire. the historian Dion Cassius He recounted the breakdown of the connection with the island, a serious problem in a period of republican instability that required reliable solutions.
The construction combined materials and techniques common in Rome
In execution they combined proven Roman techniques: resistant core of volcanic tuff and peperino, and coverings of travertine and brick in visible and more demanding areas. The use of opus caementicium It made it possible to save material without losing strength, while the travertine voussoirs reinforced the arches. The bridge, narrow by today’s standards, was sufficient to support centuries of traffic and today retains its pedestrian capacity, confirming the suitability of the design for its function.
The visible elements completed the reading of the whole with four-sided hermes on the parapets, known as four capital letterswho ordered the access. The documented restorations, including that of 1679 under Innocent XIthey reinforced the secondary parts without altering the framework of the arches and piers. This material continuity explains why the work retains its essential layout and continues to fulfill its function in the contemporary urban landscape of Rome.


